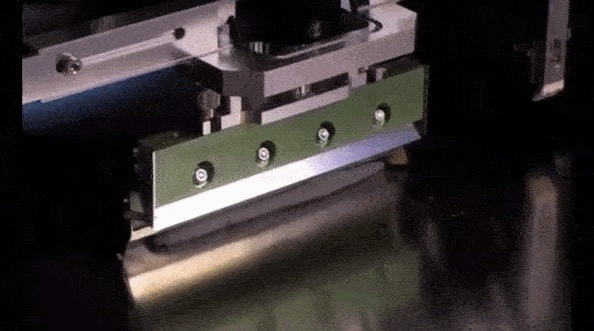
The squeegee speed used in solder paste printing is a critical parameter that can significantly affect the quality and consistency of the solder paste deposition. The appropriate squeegee speed depends on several factors, including the type of solder paste, stencil design, and the printing equipment being used. Here are some general guidelines:
In practice, it's common to start with a moderate squeegee speed and then adjust it incrementally based on visual inspection and measurement of solder paste deposits on test boards. The goal is to achieve uniform, consistent, and accurate solder paste deposition without defects like insufficient or excess solder paste.
Remember that fine-pitch components and tight PCB layouts may require slower squeegee speeds to ensure precise paste placement, while larger components and less complex layouts may tolerate higher speeds. It's important to establish a well-controlled printing process with defined parameters to maintain consistent results in production.
- Solder Paste Type: Different solder pastes have varying rheological properties, including viscosity and tackiness. The ideal squeegee speed may vary depending on the specific solder paste being used. Consult the solder paste manufacturer's recommendations for optimal printing parameters.
- Stencil Design: The design of the stencil, including aperture sizes, shapes, and thickness, can influence the squeegee speed. Fine-pitch apertures may require slower squeegee speeds to ensure proper paste release, while larger apertures may tolerate higher speeds.
- Squeegee Blade Type: The type of squeegee blade, such as metal or polyurethane, can impact the printing process. Different blade materials may perform optimally at different speeds, so consider the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Design: The PCB layout, including pad sizes, spacing, and component orientation, can affect the choice of squeegee speed. Boards with fine-pitch components may require slower speeds to prevent bridging or solder paste smearing.
- Squeegee Pressure: Squeegee pressure, which determines the force applied during the printing process, is closely related to squeegee speed. Adjusting the pressure may allow you to fine-tune the printing process to achieve optimal results at a specific speed.
- Printing Equipment: Different solder paste printers have varying capabilities and control systems. Some printers may offer a wider range of squeegee speed adjustment, while others may have limitations. Consult the equipment manual for recommended speed settings.
- Environmental Conditions: The temperature and humidity in the printing environment can affect solder paste viscosity and tackiness. These conditions may influence the optimal squeegee speed, so monitor environmental factors during printing.
- Process Validation: Conduct process validation and optimization experiments to determine the best squeegee speed for your specific application. Perform test prints with different speed settings and evaluate the solder paste deposition quality, including print consistency and solder joint quality.
In practice, it's common to start with a moderate squeegee speed and then adjust it incrementally based on visual inspection and measurement of solder paste deposits on test boards. The goal is to achieve uniform, consistent, and accurate solder paste deposition without defects like insufficient or excess solder paste.
Remember that fine-pitch components and tight PCB layouts may require slower squeegee speeds to ensure precise paste placement, while larger components and less complex layouts may tolerate higher speeds. It's important to establish a well-controlled printing process with defined parameters to maintain consistent results in production.