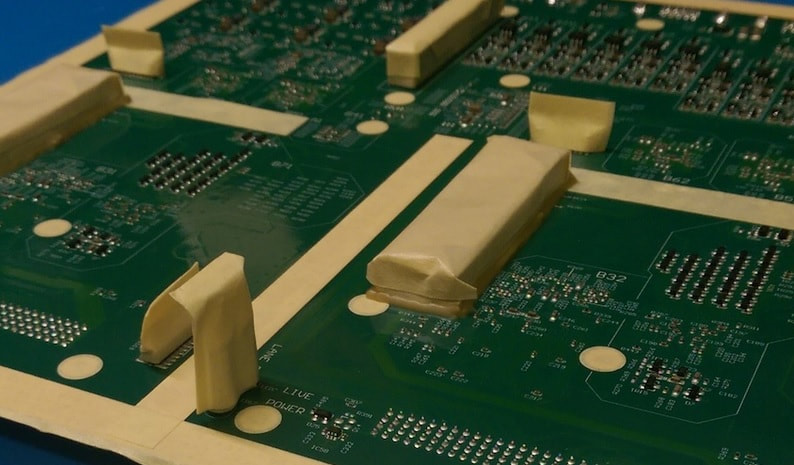
Masking is an important step in the conformal coating process to protect certain areas of a printed circuit board (PCB) or electronic assembly from being coated. This is necessary when certain components or areas should not be covered with the conformal coating material. Here's a general guide on the process of masking before conformal coating:
- Identify Components to be Masked:
- Review the PCB design and identify the components or areas that should not be coated. These may include connectors, switches, test points, sensitive electronic components, or any part where coating could interfere with functionality.
- Select Appropriate Masking Materials:
- Choose masking materials suitable for the conformal coating process and the specific components being protected. Common masking materials include:
- Masking tapes: Specialized tapes designed to resist conformal coating chemicals and ensure clean removal.
- Liquid masking materials: Brush-on or spray-on materials that can be applied to specific areas and later peeled or washed off.
- Choose masking materials suitable for the conformal coating process and the specific components being protected. Common masking materials include:
- Clean the PCB:
- Ensure the PCB is thoroughly cleaned before applying any masking material. Cleaning removes contaminants and residues that could affect the adhesion of the masking material.
- Apply Masking Material:
- For masking tapes, carefully apply them over the components or areas that need protection. Ensure that the tape adheres securely and completely covers the target surfaces.
- If using liquid masking materials, carefully apply the material using a brush, applicator, or spray. Ensure an even and complete coverage over the designated areas. Allow the liquid masking material to dry or cure according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Precision and Attention to Detail:
- Take care to apply masking materials with precision, especially in areas with fine pitch components or tight clearances. Attention to detail is crucial to prevent coating from seeping under the mask.
- Multiple Layers if Necessary:
- In some cases, multiple layers of masking material may be necessary to ensure complete coverage and protection. Follow the recommended layering guidelines provided by the masking material manufacturer.
- Inspect Masked Areas:
- After masking, inspect the protected areas to ensure that the masking materials are securely in place and cover all the required surfaces. Look for any gaps or areas that might be vulnerable to coating.
- Conformal Coating Application:
- Proceed with the conformal coating process, whether it involves spraying, dipping, or brushing, while ensuring that the masked areas remain protected.
- Remove Masking After Coating:
- Once the conformal coating has been applied and cured, carefully remove the masking materials. Peel off masking tapes or wash away liquid masking materials, taking care not to damage the coated or uncoated surfaces.
- Final Inspection:
- Inspect the entire assembly for any signs of incomplete masking or coating defects. Perform any necessary touch-up work if issues are identified.
- Inspect the entire assembly for any signs of incomplete masking or coating defects. Perform any necessary touch-up work if issues are identified.
Following these steps helps ensure that conformal coating is applied precisely where it's needed, protecting the critical components while allowing the coated areas to provide the desired environmental protection.