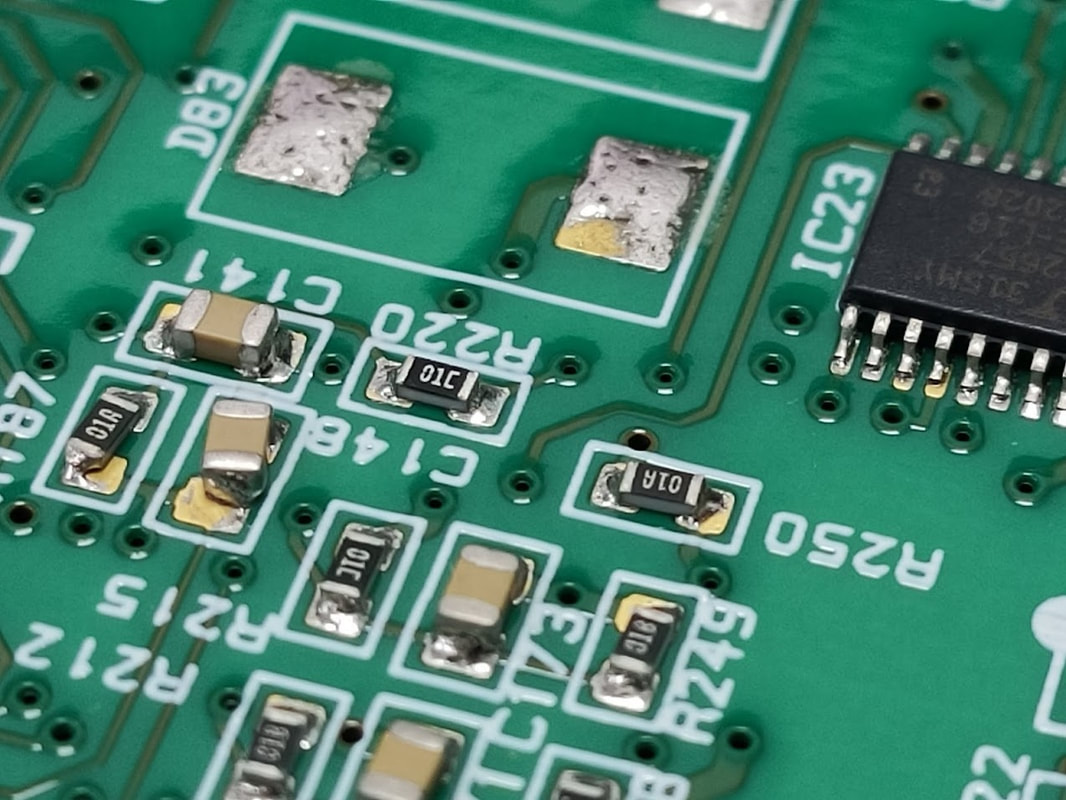
Surface mount PCBs can experience poor solderability for various reasons. Solderability issues can lead to weak or inconsistent solder joints, which can affect the overall functionality and reliability of the electronic assembly. Some common factors that can contribute to poor solderability on surface mount PCBs include:
- Oxidation: One of the most common reasons for poor solderability is oxidation of the metal surfaces to be soldered. The most commonly used materials for surface mount components are copper and tin-lead or lead-free solder. When these materials are exposed to air, they can form an oxide layer, which makes soldering difficult. Proper storage and handling techniques are essential to prevent oxidation.
- Contamination: Surface mount components or PCBs can become contaminated with oils, dust, or other debris during manufacturing, handling, or storage. Contaminants can prevent proper solder wetting and adhesion.
- Incorrect solder paste: Using the wrong type or outdated solder paste can lead to poor solderability. Solder paste has a limited shelf life, and using expired or improperly stored paste can result in soldering issues.
- Insufficient or excessive solder paste: Applying too little or too much solder paste to the pads can lead to solderability problems. Inadequate paste may not create proper solder fillets, while excessive paste can cause solder bridges or tombstoning.
- Inadequate temperature profiles: Incorrect reflow soldering profiles, including preheat, soak, reflow, and cooling stages, can lead to poor solderability. These profiles need to match the specifications of the solder paste and components.
- Component and pad design: Poor component design, including incorrect pad sizes or spacing, can affect solderability. Component packages may also play a role in solderability issues.
- Incompatible materials: Mixing materials that are not compatible with each other, such as using lead-free solder with components that have tin-lead finishes, can lead to solderability issues.
- Flux-related issues: Flux is essential for the soldering process, as it removes oxides and promotes wetting. Using the wrong type of flux or using contaminated flux can lead to solderability problems.
- Solder mask problems: Solder mask misalignment or defects can expose pads to oxidation, contamination, or other issues that affect solderability.
To address poor solderability on surface mount PCBs, you may need to consider various solutions, such as using proper storage and handling procedures, inspecting and cleaning components and PCBs, verifying the quality of solder paste and flux, optimizing reflow profiles, and ensuring that component and pad designs are suitable for soldering processes. Identifying the specific cause of the solderability issue is essential for implementing the appropriate corrective measures.