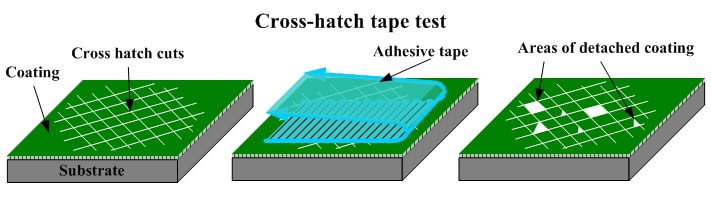
Adhesion testing is a way of assessing the effectiveness of conformal coating on a substrate. The purpose of this test is to evaluate how well the coating adheres to the surface of the electronic assembly. There are various methods to perform adhesion testing, but one common approach is the tape test. Here's an explanation of the adhesion test process:
Materials and Equipment:
- Pressure-Sensitive Tape:
- Use a standardized pressure-sensitive tape, such as ASTM D3359 Type II or similar.
- Test Equipment:
- Adhesion test equipment, which typically includes a device for applying uniform pressure during the tape removal process.
- Prepare the Test Specimen:
- Cut the conformally coated electronic assembly into test panels or sections. Ensure that the coating thickness on these panels is representative of the overall assembly.
- Cross-Hatch or Grid Pattern:
- Use a sharp blade to create a cross-hatch or grid pattern on the coated surface. The pattern typically consists of parallel lines forming squares or diamonds. Common specifications include 1mm or 2mm spacing.
- Apply Tape:
- Place the pressure-sensitive tape over the cross-hatched area. Ensure good contact by applying uniform pressure using the appropriate test equipment.
- Tape Removal:
- After applying the tape, remove it swiftly at a 180-degree angle from the surface. The rate of removal and angle should be consistent throughout the test.
- Inspection:
- Examine the cross-hatched area for any coating removal. Assess the percentage of the grid or squares that remain intact. Use a magnifying glass if needed to ensure accurate evaluation.
- Adhesion Rating:
- Typically, adhesion ratings are assigned based on the percentage of coating removed. Common adhesion ratings range from 5B (no coating removed) to 0B (more than 65% coating removed). The specific criteria may vary based on industry standards or specifications.
- 5B: Excellent Adhesion: No coating is removed.
- 4B: Good Adhesion: Slight flaking or removal at the edges.
- 3B: Fair Adhesion: Coating removal up to 10%.
- 2B: Poor Adhesion: Coating removal between 10% and 35%.
- 1B: Very Poor Adhesion: Coating removal between 35% and 65%.
- 0B: No Adhesion: More than 65% coating removal.
The adhesion test helps ensure that the conformal coating adheres well to the substrate and provides the necessary protection against environmental factors. It is important to follow relevant industry standards and specifications for performing and interpreting adhesion test results.